Virtualization
- Emulation basics
- Virtualization basics
- Paravirtualization basics
- Hardware support for virtualization
- Overview of the Xen hypervisor
- Overview of the KVM hypervisor
Emulation basics
- Instructions are emulated (each time they are executed)
- The other system components are also emulated:
- MMU
- Physical memory access
- Peripherals
- Target architecture - the architecture that it is emulated
- Host architecture - the architecture that the emulator runs on
- For emulation target and host architectures can be different
Virtualization basics
- Defined in a paper by Popek & Goldberg in 1974
- Fidelity
- Performance
- Security
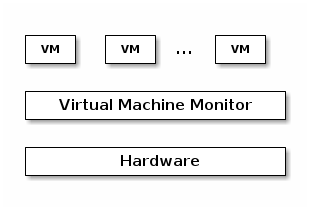
Classic virtualization
- Trap & Emulate
- Same architecture for host and target
- Most of the target instructions are natively executed
- Target OS runs in non-privilege mode on the host
- Privileged instructions are trapped and emulated
- Two machine states: host and guest
Software virtualization
- Not all architecture can be virtualized; e.g. x86:
- CS register encodes the CPL
- Some instructions don't generate a trap (e.g. popf)
- Solution: emulate instructions using binary translation
MMU virtualization
- "Fake" VM physical addresses are translated by the host to actual physical addresses
- Guest virtual address -> Guest physical address -> Host Physical Address
- The guest page tables are not directly used by the host hardware
- VM page tables are verified then translated into a new set of page tables on the host (shadow page tables)
Shadow page tables
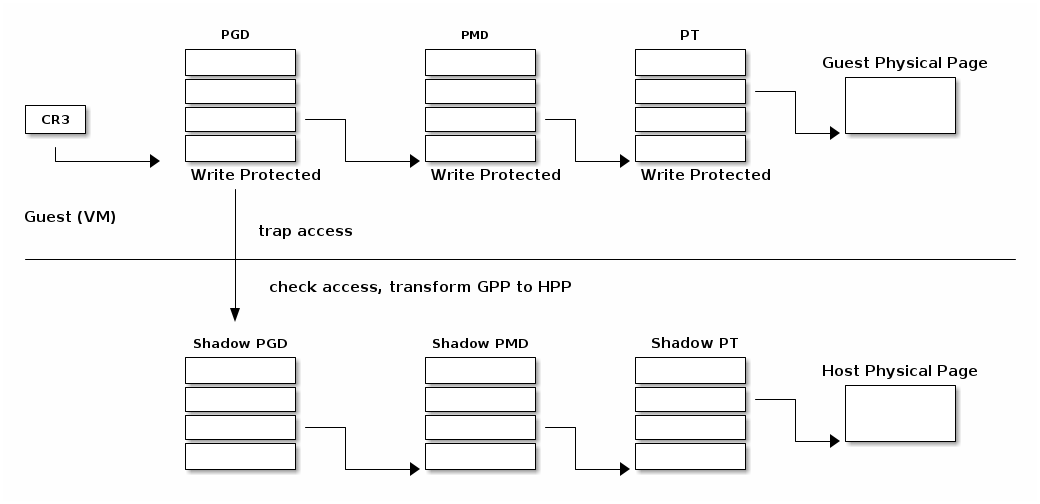
Lazy shadow sync
- Guest page tables changes are typically batched
- To avoid repeated traps, checks and transformations map guest page table entries with write access
- Update the shadow page table when
- The TLB is flushed
- In the host page fault handler
I/O emulation
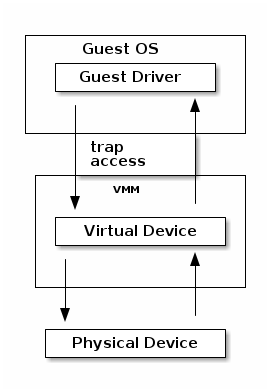
Example: qemu SiFive UART emulation
/*
* QEMU model of the UART on the SiFive E300 and U500 series SOCs.
*
* Copyright (c) 2016 Stefan O'Rear
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms and conditions of the GNU General Public License,
* version 2 or later, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for
* more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with
* this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
#include "qemu/osdep.h"
#include "qapi/error.h"
#include "qemu/log.h"
#include "chardev/char.h"
#include "chardev/char-fe.h"
#include "hw/irq.h"
#include "hw/char/sifive_uart.h"
/*
* Not yet implemented:
*
* Transmit FIFO using "qemu/fifo8.h"
*/
/* Returns the state of the IP (interrupt pending) register */
static uint64_t uart_ip(SiFiveUARTState *s)
{
uint64_t ret = 0;
uint64_t txcnt = SIFIVE_UART_GET_TXCNT(s->txctrl);
uint64_t rxcnt = SIFIVE_UART_GET_RXCNT(s->rxctrl);
if (txcnt != 0) {
ret |= SIFIVE_UART_IP_TXWM;
}
if (s->rx_fifo_len > rxcnt) {
ret |= SIFIVE_UART_IP_RXWM;
}
return ret;
}
static void update_irq(SiFiveUARTState *s)
{
int cond = 0;
if ((s->ie & SIFIVE_UART_IE_TXWM) ||
((s->ie & SIFIVE_UART_IE_RXWM) && s->rx_fifo_len)) {
cond = 1;
}
if (cond) {
qemu_irq_raise(s->irq);
} else {
qemu_irq_lower(s->irq);
}
}
static uint64_t
uart_read(void *opaque, hwaddr addr, unsigned int size)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = opaque;
unsigned char r;
switch (addr) {
case SIFIVE_UART_RXFIFO:
if (s->rx_fifo_len) {
r = s->rx_fifo[0];
memmove(s->rx_fifo, s->rx_fifo + 1, s->rx_fifo_len - 1);
s->rx_fifo_len--;
qemu_chr_fe_accept_input(&s->chr);
update_irq(s);
return r;
}
return 0x80000000;
case SIFIVE_UART_TXFIFO:
return 0; /* Should check tx fifo */
case SIFIVE_UART_IE:
return s->ie;
case SIFIVE_UART_IP:
return uart_ip(s);
case SIFIVE_UART_TXCTRL:
return s->txctrl;
case SIFIVE_UART_RXCTRL:
return s->rxctrl;
case SIFIVE_UART_DIV:
return s->div;
}
qemu_log_mask(LOG_GUEST_ERROR, "%s: bad read: addr=0x%x\n",
__func__, (int)addr);
return 0;
}
static void
uart_write(void *opaque, hwaddr addr,
uint64_t val64, unsigned int size)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = opaque;
uint32_t value = val64;
unsigned char ch = value;
switch (addr) {
case SIFIVE_UART_TXFIFO:
qemu_chr_fe_write(&s->chr, &ch, 1);
update_irq(s);
return;
case SIFIVE_UART_IE:
s->ie = val64;
update_irq(s);
return;
case SIFIVE_UART_TXCTRL:
s->txctrl = val64;
return;
case SIFIVE_UART_RXCTRL:
s->rxctrl = val64;
return;
case SIFIVE_UART_DIV:
s->div = val64;
return;
}
qemu_log_mask(LOG_GUEST_ERROR, "%s: bad write: addr=0x%x v=0x%x\n",
__func__, (int)addr, (int)value);
}
static const MemoryRegionOps uart_ops = {
.read = uart_read,
.write = uart_write,
.endianness = DEVICE_NATIVE_ENDIAN,
.valid = {
.min_access_size = 4,
.max_access_size = 4
}
};
static void uart_rx(void *opaque, const uint8_t *buf, int size)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = opaque;
/* Got a byte. */
if (s->rx_fifo_len >= sizeof(s->rx_fifo)) {
printf("WARNING: UART dropped char.\n");
return;
}
s->rx_fifo[s->rx_fifo_len++] = *buf;
update_irq(s);
}
static int uart_can_rx(void *opaque)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = opaque;
return s->rx_fifo_len < sizeof(s->rx_fifo);
}
static void uart_event(void *opaque, QEMUChrEvent event)
{
}
static int uart_be_change(void *opaque)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = opaque;
qemu_chr_fe_set_handlers(&s->chr, uart_can_rx, uart_rx, uart_event,
uart_be_change, s, NULL, true);
return 0;
}
/*
* Create UART device.
*/
SiFiveUARTState *sifive_uart_create(MemoryRegion *address_space, hwaddr base,
Chardev *chr, qemu_irq irq)
{
SiFiveUARTState *s = g_malloc0(sizeof(SiFiveUARTState));
s->irq = irq;
qemu_chr_fe_init(&s->chr, chr, &error_abort);
qemu_chr_fe_set_handlers(&s->chr, uart_can_rx, uart_rx, uart_event,
uart_be_change, s, NULL, true);
memory_region_init_io(&s->mmio, NULL, &uart_ops, s,
TYPE_SIFIVE_UART, SIFIVE_UART_MAX);
memory_region_add_subregion(address_space, base, &s->mmio);
return s;
}
Paravirtualization
- Change the guest OS so that it cooperates with the VMM
- CPU paravirtualization
- MMU paravirtualization
- I/O paravirtualization
- VMM exposes hypercalls for:
- activate / deactivate the interrupts
- changing page tables
- accessing virtualized peripherals
- VMM uses events to trigger interrupts in the VM
Intel VT-x
- Hardware extension to transform x86 to the point it can be virtualized "classically"
- New execution mode: non-root mode
- Each non-root mode instance uses a Virtual Machine Control Structure (VMCS) to store its state
- VMM runs in root mode
- VM-entry and VM-exit are used to transition between the two modes
Virtual Machine Control Structure
- Guest information: state of the virtual CPU
- Host information: state of the physical CPU
- Saved information:
- visible state: segment registers, CR3, IDTR, etc.
- internal state
- VMCS can not be accessed directly but certain information can be accessed with special instructions
VM entry & exit
- VM entry - new instructions that switches the CPU in non-root mode and loads the VM state from a VMCS; host state is saved in VMCS
- Allows injecting interrupts and exceptions in the guest
- VM exit will be automatically triggered based on the VMCS configuration
- When VM exit occurs host state is loaded from VMCS, guest state is saved in VMCS
VM execution control fields
- Selects conditions which triggers a VM exit; examples:
- If an external interrupt is generated
- If an external interrupt is generated and EFLAGS.IF is set
- If CR0-CR4 registers are modified
- Exception bitmap - selects which exceptions will generate a VM exit
- IO bitmap - selects which I/O addresses (IN/OUT accesses) generates a VM exit
- MSR bitmaps - selects which RDMSR or WRMSR instructions will generate a VM exit
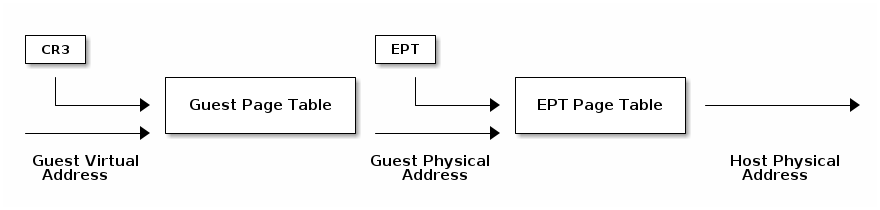
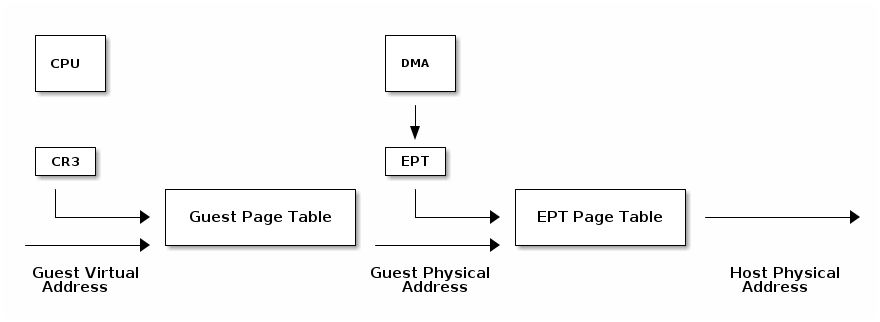
Extend Page Tables
- Reduces the complexity of MMU virtualization and improves performance
- Access to CR3, INVLPG and page faults do not require VM exit anymore
- The EPT page table is controlled by the VMM
VPID
- VM entry and VM exit forces a TLB flush - loses VMM / VM translations
- To avoid this issue a VPID (Virtual Processor ID) tag is associated with each VM (VPID 0 is reserved for the VMM)
- All TLB entries are tagged
- At VM entry and exit just the entries associated with the tags are flushed
- When searching the TLB just the current VPID is used
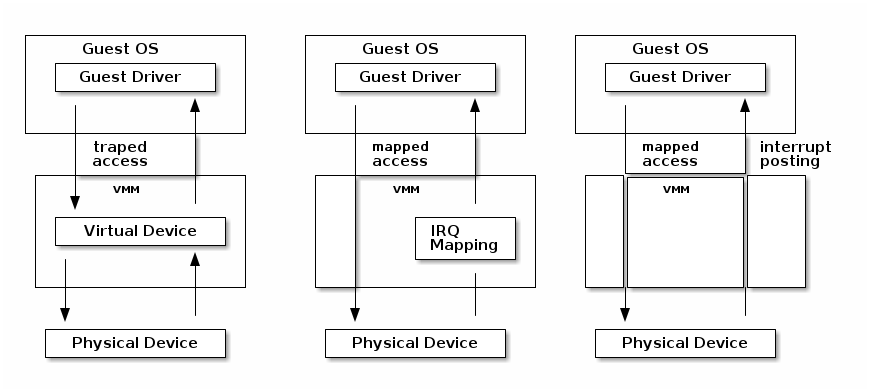
I/O virtualization
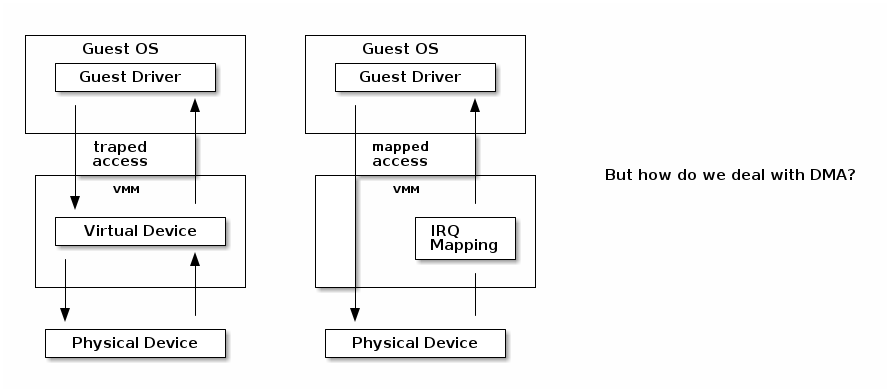
I/O MMU
VT-d protects and translates VM physical addresses using an I/O MMU (DMA remaping)
Interrupt posting
- Messsage Signaled Interrupts (MSI) = DMA writes to the host address range of the IRQ controller (e.g. 0xFEExxxxx)
- Low bits of the address and the data indicate which interrupt vector to deliver to which CPU
- Interrupt remapping table points to the virtual CPU (VMCS) that should receive the interrupt
- I/O MMU will trap the IRQ controller write and look it up in the
interrupt remmaping table
- if that virtual CPU is currently running it will take the interrupt directly
- otherwise a bit is set in a table (Posted Interrupt Descriptor table) and the interrupt will be inject next time that vCPU is run
I/O virtualization
SR-IOV
- Single Root - Input Output Virtualization
- Physical device with multiple Ethernet ports will be shown as multiple device on the PCI bus
- Physical Function is used for the control and can be configured
- to present itself as a new PCI device
- which VLAN to use
- The new virtual function is enumerated on the bus and can be assigned to a particular guest
qemu
- Uses binary translation via Tiny Code Generator (TCG) for efficient emulation
- Supports different target and host architectures (e.g. running ARM VMs on x86)
- Both process and full system level emulation
- MMU emulation
- I/O emulation
- Can be used with KVM for accelerated virtualization
KVM
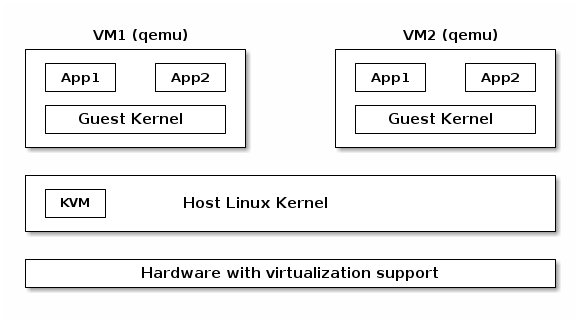
KVM
- Linux device driver for hardware virtualization (e.g. Intel VT-x, SVM)
- IOCTL based interface for managing and running virtual CPUs
- VMM components implemented inside the Linux kernel (e.g. interrupt controller, timers)
- Shadow page tables or EPT if present
- Uses qemu or virtio for I/O virtualization
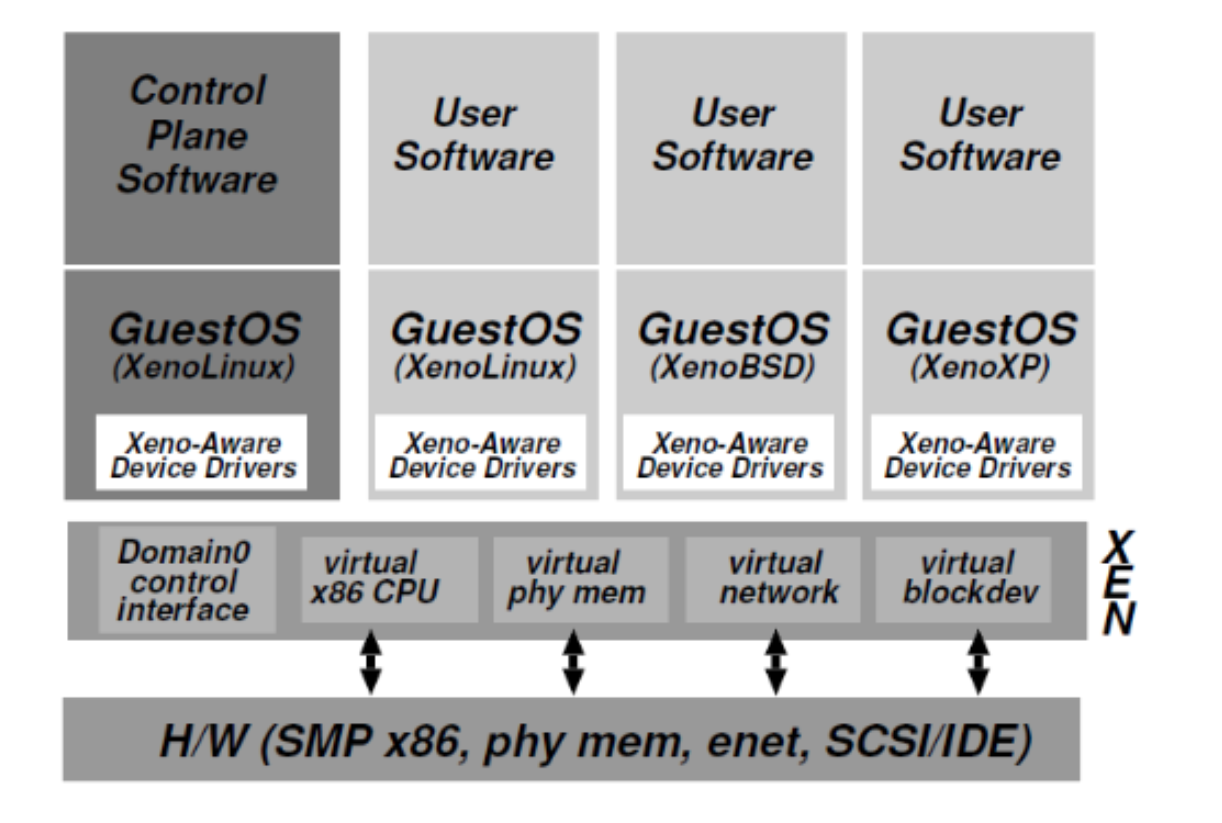
Xen
- Type 1 = Bare Metal Hypervisor
- Type 2 = Hypervisor embedded in an exist kernel / OS
Xen